Aromatic isocyanates – TDI / MDI
This page describes aromatic isocyanates, more precisely Toluene diisocyanate. ( TDI ) And Diphenylmethane diisocyanate ( MDI It brings together basic information about ) ) , their physical properties, health effects, detection tools (aromatic isocyanate gas detector) and appropriate respiratory protection equipment (gas mask or PAPR with combined filter type E-P2).
Properties of aromatic isocyanates (TDI – MDI)
Aromatik izosiyanatlar Today it is used in polyurethane synthesis. Toluene diisocyanate , TDI Also called , it is mainly used in the production of flexible filling foams. Diphenylmethane diisocyanate , MDI Also called , it is useful in the production of rigid foams for insulation and can also be used as a binder in foundries.
- GAS
- TDI
- 4,4′-MDI
- CAS
- 26471-62-5
- 101-68-8
- TWA (8 hours)
- 0,01 ppm
- 0,01 ppm
- SETUP (15 minutes)
- 0,02 ppm
- 0,02 ppm
- LEL
- %0,9
- –
- IP
- –
- –
- DENSITY/AIR
- 6
- 8.5
- FILTER/SCBA
- A2B2, P3
- One, P3
Health effects of aromatic isocyanates
TDI ( Toluene Diisocyanate ) is a colorless or pale yellow liquid with a pungent, penetrating odor detectable at low concentrations (range 1 to 2 ppm). 4,4′-MDI ( Diphenylmethane diisocyanate ), in the form of white or pale yellow crystals with a slightly musty odor.
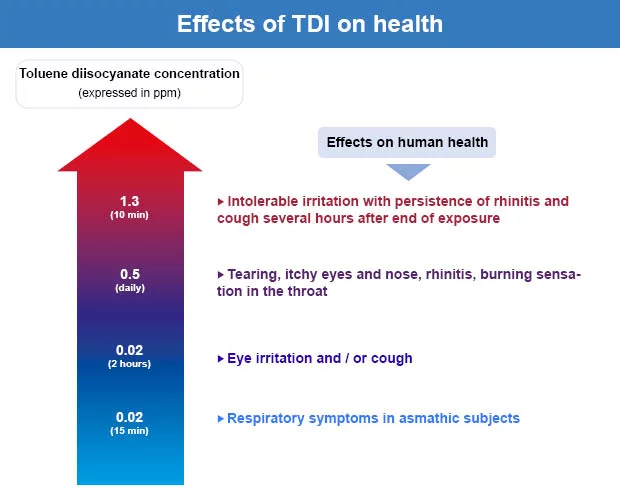
Acute exposure to TDI and MDI isocyanates causes damage to respiratory mucous membranes that can be serious. Skin and eye irritation can also be particularly serious. Chronic exposure to TDI can cause occupational asthma and rapid decline of respiratory function. Repeated MDI exposure causes allergic manifestations: eczema, asthma, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, conjunctivitis.
Short-term exposure to high concentrations of MDI can cause reactions that can occur after several hours: irritation of mucous membranes (conjunctivitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, nausea, vomiting), skin irritation, lung irritation (chest pain, cough, etc.), neurological disorders ( dizziness, disturbances of balance and consciousness, headaches) and, in the most severe cases, pulmonary edema.
In case of repeated exposure to low concentrations of MDI, reactions can occur from several weeks to several years: contact eczema, allergic asthma or even hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
Aromatic isocyanate detectors (TDI MDI)
Monitoring aromatic isocyanates Little equipment is available for : passive chemical detection badges for workers to wear, or the much more complex (expensive) optical gas analyzer.
Aromatic isocyanates respiratory protection (TDI MDI)
Since isocyanates are very irritating to the eyes and respiratory tract, a full-face mask or mask should be used for short interventions or in rooms with low gas concentrations. with A2B2-P3 combined filter for TDI or with A-P3 for MDI It is recommended to choose a motorized air purifying respirator (more comfortable). In case of emergency interventions, a self-contained breathing apparatus will be mandatory.